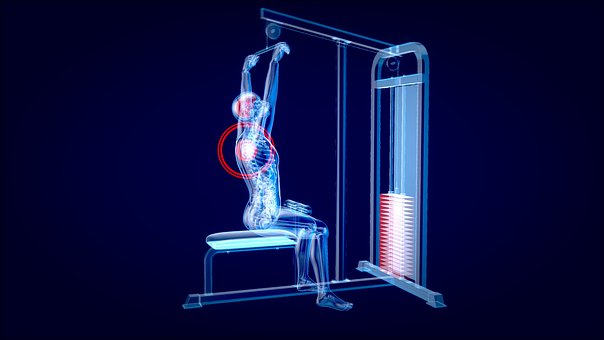
One of the most popular exercises for strengthening the muscles of the back is the lat pulldown.
There is less research on the lat pulldown than other exercises like the squat or bench press, but there is still a lot of evidence that it works well for muscles in the back and arms.
There are several varieties of lat pulldown exercises, including but not limited to close-grip, wide-grip, reverse-grip (supination), and neutral-grip pulldowns.
Analyzing The Lat Pulldown
This exercise targets the latissimus dorsi muscle of the back. There are several primary joint actions that occur during the lat pulldown, though there may also be some accessory motions depending on how the person doing the exercise performs it.
Concentric Phase (pulling bar towards the chest)
- Shoulder adduction
- Shoulder horizontal abduction
- Elbow flexion
- Scapulae downward rotation
- Scapulae retraction
Eccentric Phase (returning to the start position)
- Shoulder abduction
- Shoulder horizontal adduction
- Elbow extension
- Scapulae upward rotation
- Scapulae protraction
The way a muscle is activated – whether it is contracting eccentrically or concentrically – as well as the technique the exerciser chooses, affects how the muscle works.
Lat Pulldown: Muscles Worked
Agonist
-Latissimus Dorsi (largest back muscle)
The Teres Major is a muscle located near the bottom portion of the shoulder blade.
Synergist
-Posterior Deltoid (back of the shoulder muscle)
The trapezius muscle is a large muscle in the back that is shaped like a trapezoid. It is made up of three parts: the upper, middle, and lower trapezius.
The Rhomboid muscle connects the shoulder blade to the spine and aids in shoulder blade movement, helping to stabilize the shoulder blade to the spine and aiding in shoulder blade movement.
The Levator Scapulae is a muscle located near the side and back of the neck that is responsible for moving the scapulae.
-Biceps Brachii (front of upper arm muscle)
-Brachialis /Brachioradialis (forearm muscles)
Stabilizers
-Triceps brachii (back of upper arm muscle)
tears can cause shoulder pain. Rotator cuff tears can cause pain in the shoulder area.
A muscle is said to be eccentric when it contracts while lengthening. This usually occurs when the muscle is returning from a shortened (concentric) position to its natural resting position. An isometrics contraction is where muscle tension develops without any visible movement in the angle of the joint.
An example of concentric muscle contraction would be when you are doing a bicep curl and your arm is getting closer to your body.
How to Do the Straight-Arm Pulldown
To perform a straight-arm pulldown, stand in an upright position and grasp a straight bar or rope attachment attached to a cable pulley system. Keeping your arms straight, pull the bar or rope down until it reaches your thighs.
Step 1 — Set Up
After you have chosen the weight you would like to lift, attach the corresponding bar or rope to the top of the pulley system. This will give you the ability to complete the full range of motion for that particular weight. Hold the attachment with your hands roughly shoulder-width apart and step back until you feel the tension in the band. Bend forward at your waist until you feel a stretch in your back muscles.
A good way to keep your shoulders externally rotated is to have the inside of your upper arm face your torso.
Step 2 — Pull Down
When the bar reaches your thighs, explosively reverse the motion back up Keep a slight bend in your arms and bring the bar down towards your body. Bring the bar to your thighs, and then explosively reverse the motion back up. Your arms should remain mostly straight. Make sure the attachment is close to or touching your upper thighs.
To get the most out of this workout, start by depressing your shoulders, then bring your arms down and back.
Step 3 — Reverse and Control
Start by reversing the motion and returning the handle to the starting position. Make sure you are in full control throughout the entire eccentric portion of the lift.
If you feel like your lats aren’t working as hard as they could be, try changing the angle of your torso.
Straight-Arm Pulldown Sets and Reps
There are other exercises that may be more effective for enhancing strength, but the straight-arm pulldown is a good movement to build your lats and increase training volume. Isolation exercises like the straight-arm pulldown are 300% more effective when performed with higher repetitions and an emphasis on time under tension.
- To Build Muscle: Perform 2-4 sets of 10-20 repetitions with a moderate load and controlled tempo.
- To Warm-Up or Pre-Exhaust: Perform 1-2 sets of 10-15 repetitions with a lighter load to engage your lats.
Common Straight-Arm Pulldown Mistakes
This exercise is not complicated, but it can be done incorrectly. If you’re planning to use this exercise to help you achieve a bigger back, you should make sure you’re doing it in the most effective way possible and that it aligns with your goals.
Going Too Heavy
There is no need to put too much strain on your muscles during the straight-arm pulldown. The purpose of accessory movements is to target a specific body part and build it up. Lifting too much weight might cause you to use different muscles to finish the movement. Use lighter weights and less effort for your isolation exercises. You should use heavier weights and put in maximal effort for your compound exercises while using lighter weights and less effort for your isolation exercises.
Not Focusing On the Muscle
The intent of training for strength is to increase the amount of force that can be produced by the muscles, whereas the intent of training for hypertrophy is to increase the size of the muscles. In strength training, you aim to move a heavy load from one point to another. If you’re training for speed or power, you want to be able to move the weight quickly.
You want to produce high levels of metabolic stress and stimulate as many muscle fibers as possible in order to build muscle. If you let the triceps take over during the straight-arm pulldown, it will reduce the tension on the lats and make the movement less effective.
Going Too Light
The goal of training is to induce an adaptation. If you continue using the same exercise with the same weight, your body will eventually get used to it. Even though you don’t need to go too heavy with the straight-arm pulldown, you should still strive to increase the weight you use over time.
In order to keep progressing with this movement, you’ll need to do one of the following: increase the weight, increase the volume, or adjust the way you perform the repetition. Even though accessory movements may not be as exciting as heavy barbell lifts, don’t slack off on them.
Straight-Arm Pulldown Variations
While the basics are always a good choice, a bit of novelty can be fun. There are many ways to make the traditional straight-arm pulldown more challenging, such as adjusting your grip placement, switching the attachment, or slightly altering the bar path.
Kayak Pulldown
This exercise is a combination of a traditional straight-arm pulldown and a kayak row. The kayak stroke gives you a greater range of motion and allows you to really feel your lats working.
The straight-arm pulldown is the perfect exercise to alternate with if you want to create a strong back pump and work your lats.
Unilateral Straight-Arm Pulldown
Training that uses both sides of the body has many benefits, but every program should also use training that focuses on one side of the body. The straight-arm pulldown with one arm is more effective because you can go through a greater range of motion than with two arms, which could help with muscle growth.
The straight-arm pulldown is a good exercise to do if you want to highlight any imbalances in your non-dominant arm.
Straight-Arm Pulldown Alternatives
There are many other exercises you can do to target and develop your back muscles. The lying pullover and chest-supported pulldown are both exercises that work the lats directly and provide a new stimulus for your body to adapt to.
Dumbbell Pullover
The seated cable row is a great alternative to the cable tree and will still allow you to train your lats through an extension pattern. The dumbbell pullover is a great free-weight choice for focusing on your lats and training the movement of shoulder extension.
This exercise provides a good stretch for the lats and works the muscle through its full range of motion. You can use a dumbbell, a kettlebell, or even a medicine ball for this exercise.
Chest-Supported Straight-Arm Pulldown
Chest-supported exercises are less likely to cause cheating or injury than other exercises. They often work well for people who have lower back pain or other injuries. If you want to focus the tension on your back, do the chest-supported straight-arm pulldown. You’ll be resting on a bench and won’t be using your legs, which could help your technique by keeping additional body parts or extra momentum out of the equation.
Benefits of the Straight-Arm Pulldown
Isolates Your Lats
Some people pull too hard on their main exercises and get help from their shoulders, biceps, and momentum. Because of what? The individual back muscles might not be getting the attention they deserve.
Hypertrophy (muscle growth) occurs when there is stress on the muscles, recruitment of muscle fibers, and tension on the muscle. strength = the ability to exert force to overcome resistance muscle gain = an increase in muscle mass If you want to focus on specific body parts that are lagging behind or you want to create a more symmetrical physique, you should add isolation exercises to your workout routine.
Serves As a Solid Warm-Up
If you want to be able to bench press a lot of weight, you’ll need to have a strong back. Your shoulder is the most mobile joint in your body, so your upper back will provide the stability you need to press safely and effectively.
Keeping your lats engaged and pulling the bar to your chest will help improve your form and bench total. The straight-arm pulldown is a great exercise to perform before you start your bench press routine. This exercise will help to strengthen your shoulders, which will in turn help you to prevent injuries when performing the bench press.
Grip Positions For The Lat Pulldown
There are different ways you can hold the bar when doing lat pulldowns. The various grip positions for pull-ups are as follows: a pronated grip with the hands close together (narrower than shoulder width), a pronated grip with the hands far apart (wider than shoulder width), a neutral grip with the hands close together, a neutral grip with the hands far apart, and a supinated grip.
Research Concerning Grip Position
There is disagreement among fitness professionals about whether a wide grip or a narrow grip is more effective for activating the latissimus dorsi and other muscles. So, Andersen et al. researched whether… Fifteen men participated in the study. The researchers used electromyographic (EMG) activity to compare three different pronated grip widths: close, medium, and wide grips (1, 1.5, and 2 times biacromial distance). The latissumis dorsi was similarly activated during the concentric phase of the exercise regardless of grip. The biceps brachii was more active when using a narrower or medium grip, compared to a wide grip.
Lastly, the exercise resulted in greater activation of the latissimus dorsi muscle when using a wide or medium grip, as compared to using a narrow grip. The researchers suggest that a medium pronated grip may be a slightly better option, but fitness enthusiasts and athletes should expect similar results in strength and muscle size no matter which grips they choose.
The length measured from the end of one shoulder to the opposite shoulder.
A technique called an electromyography is used to help assess and record the electrical activity that muscles produce.
A study in 2009 by Lusk et al. looked at different grip positions for the lat pulldown exercise. The researchers found that activation of the latissimus dorsi, middle trapezius, and biceps brachii muscle groups was greatest when using a wide-supinated grip, followed by a wide-pronated grip, a narrow-supinated grip, and then a narrow-pronated grip. Twelve men participated in the study.
They suggested that a pronated grip (both wide and narrow) activates the latissimus dorsi more than a supinated grip. There wasn’t much difference in how active the biceps brachii or middle trapezius muscles were between the different grips. The researchers found that a pronated grip is the best way to activate the latissimus dorsi.
A study was done in 2002 by Signorile, Zink, and Szwed investigated how different grip positions (close neutral-grip, close supinated grip, wide-grip front of neck, and wide-grip behind the neck) affected the electric muscle activity of shoulder muscles during the lat pull-down exercise.
The research group specifically monitored the electromyography (EMG) activity of four muscles – the latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major, teres major, and long head of the triceps brachii. The authors found numerous differences between all of the grip positions. The most significant difference was found between the underhand grip position and all of the other grip positions. The biggest activation of the latissimus dorsi happened when the wide grip was performed in front of the neck. The authors suggest using a variety of grip positions that are specific to a person’s needs and goals in order to maximize the benefits of the exercises being performed.
The latissimus dorsi may be slightly activated and strengthened by using a medium or wide pronated grip. One should not expect to see noticeable changes in strength or muscle size by choosing one grip over another. It is best to vary grip positions during the lat pulldown exercise to keep from getting bored and to make it more likely that you will stick with the exercise.
Exercise Recommendation For Lat Pulldown
For those new to exercise, the lat pulldown is an important part of a progressive and systematic approach. You should start with a lightweight when you are first starting out and focus on perfecting your technique. The main focus should be on learning to pull the shoulder blades back properly, without movement that makes up for it (for example, by thrusting the head forward or shrugging the shoulders). You should focus on using the proper technique before adding additional load or trying to lift the maximum amount possible.
Begin by gripping the barbell with your palms facing down, approximately shoulder-width apart. Since fitness enthusiasts are growing more confident, they can start to experiment with different grip positions. You should keep the volume relatively low to avoid overtraining and getting unnecessarily sore muscles.
If you are experiencing shoulder pain, you should see a doctor before continuing your exercise program. In addition to the above exercises, include resistance training exercises for the back to improve overall strength and muscle symmetry. These exercises can be a variety of open-and-closed-chain exercises.