What is Candida Overgrowth?
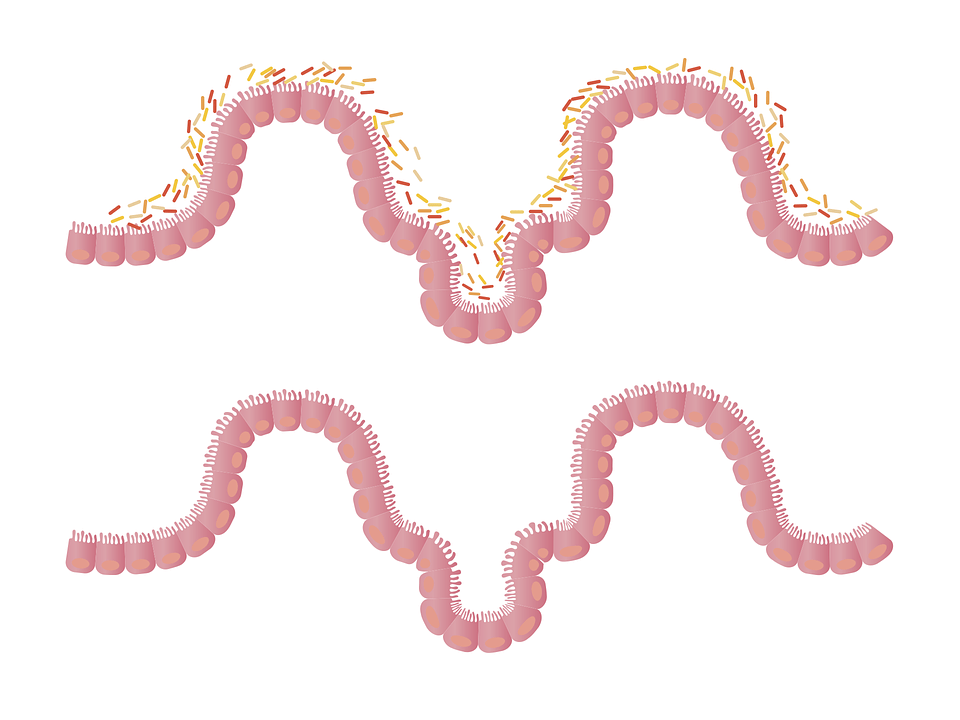
Candida is a form of fungal yeast that lives in our mouths and small intestines in very small amounts. The skin around the vagina is also part of the vaginal tract. Although it is often associated with illness, the presence of bacteria is not always negative. Bacteria are present in healthy individuals as well. This yeast is not harmful, and can actually be helpful in absorbing nutrients and aiding digestion.
If the balance of different types of bacteria, yeast, viruses, and other microorganisms in our gut is not even, things can go wrong.
The yeast that lives in our system, Candida albicans, can multiply and become too numerous. This is called Candida overgrowth. If there is too much candida in the gut, it often means that there are not enough beneficial bacteria. This can upset the overall balance of the gut microbiome.
Candida albicans is a type of yeast that is often found in the intestine. It is easy for this yeast to enter the intestine because it is often found in foods that we eat, such as bread and beer.
Candida is known to change shapes. It usually exists in a round cell structure. The bacterium can change into sharp filaments that can puncture the lining of the gut wall. When the gut lining is damaged, it makes it easier for Candida to enter the intestine. If harmful substances enter your bloodstream, it can cause a leaky gut and other symptoms of Candida.
Candida Overgrowth is quite common and has a laundry list of symptoms, which we deal with in another section, but here is a quick checklist:
- Bloating or constipation
- Rashes
- Fatigue, brain fog, or mood swings
What Are the Causes of Candida
One possible way that candida overgrowth can start is when a foreign substance enters the body and throws off the balance of bacteria in the gut microbiome.
Having a balanced microbiota is important for maintaining a healthy immune system and preventing infections. There is an imbalance in the gut microbiome and Candida infections have been associated with long-term use of antibiotics, birth control, and a diet high in refined sugars. An unhealthy microbiome can lead to Candida.
Candida Overgrowth causes include:
- Steroids
- Antibiotics
- Alcohol
- Birth control pills
- Estrogen replacement therapy
- Acute and chronic stress
- Chemotherapy
- Poor diet
- Recreational drugs
- A lack of physical activity or exercise
The causes of poor health can be traced back to poor lifestyle choices. making a conscious effort to eat correctly and exercise regularly will help improve our overall health.
Addressing these key parts of your lifestyle with a focus on holistic treatment can also be beneficial in managing Candida.
What is Candida Overgrowth Symptoms?
The below-mentioned symptoms can help you figure out whether you have candida. Then we will discuss how to treat it!
- Oral Thrush
The most common symptom of candida overgrowth is easy to detect. A condition where the fungus Candida albicans grows in your mouth is called oral thrush, according to the Mayo Clinic.
The symptoms of oral thrush include:
- White coating on the tongue, cheeks, and tonsils
- White, raised lesions on the tongue or around the mouth
- Bad breath
- Redness or soreness in the mouth
- Loss of taste
- Bleeding or cracking in the mouth
- Fungal Infections of the Skin and Nails
Candida can lead to vaginal yeast infections, Athlete’s Foot, and toenail fungus. If you experience frequent infections, especially after treatment, you might have candida.
- Chronic Fatigue
Chronic fatigue can be difficult to identify the cause of, as it can be caused by a variety of factors, not just candida. An imbalance in the immune system and digestive system, which are both candida overgrowth symptoms, can also lead to chronic fatigue.
If you are constantly tired, even after getting a full night’s sleep, it may be a sign of candida.
- Chronic Sinus Infections and Other Allergy Symptoms
Candida can lead to sinus and allergy issues, such as post-nasal drip, fever, cough, bad breath, headaches, sinus pressure, and congestion.
It can be more difficult to notice if you’re someone who regularly has allergies or sinus problems. To determine if you have the condition, read through the other symptoms carefully. This will assist you in determining if candida is the root cause.
- Strong Cravings for Sugar
If your immune system or digestive system isn’t working properly, you may not get the nutrients you need from the food you eat.
These imbalances can cause severe cravings for sugar. This makes the situation worse because sugar helps candida grow and makes the problem worse.
- Difficulty Concentrating or Focusing (Brain Fog)
Yeast infection can lead to mental issues that are often called “brain fog.” These issues can include problems focusing, lack of coordination, memory loss, and changes in mood.
Other symptoms to look for include: If you experience any of the above symptoms, it could be a sign of dehydration and you should see a doctor.
- Hormone Imbalance
Candida can produce a substance that can act like estrogen. A hormonal imbalance can have various effects on the body, including a decreased sex drive, early menopause, PMS, migraines, bloating, and weight gain.
These are also common symptoms women suffer during their periods. If you notice your symptoms are worse than normal, listen to your body.
- Weak Immune System
Earlier, we said that candida overgrowth can happen when the immune system is weakened. An imbalance in the body can cause the Immune system to stay in a weakened state until the candida is cured
If your immune system is weak, it can cause you to have many of the other symptoms on this list. If you find yourself feeling weak, sick, and fatigued often, it may be a sign that the candida in your body is overgrown.
- Digestive Problems
An overgrowth of candida can lead to an imbalance of healthy bacteria in the digestive system. If there is an imbalance of healthy bacteria in the gut, it can lead to indigestion, infections, and ulcers.
Other digestive issues that can be caused by this include constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, bloating, cramping, and other stomach issues.
- Urinary Tract Infection
While this symptom is less common, it is still worth mentioning. Candida can cause infections in the urinary tract and vagina, as well as other issues, in women.
SIBO vs. Candida Overgrowth
The main difference between SIBO and Candida overgrowth is that one is a bacterial overgrowth and the other is a yeast or fungal overgrowth. SIBO only causes digestive and gut-related symptoms, while Candida Overgrowth can cause digestive issues as well as infections of the nails, skin, mouth, and also symptoms related to energy, mood, and memory.
Here is a summary of the key differences between these two diseases. It is important to know the difference between the internet and the World Wide Web so that you feel more comfortable when using the internet. You will transition from thinking that SIBO causes Candida or that Candida causes SIBO (both of which are false) to understand their vastly distinct origins.
SIBO
- Refers to bacterial overgrowth
- Bacteria that usually inhabit the large intestine and colon now multiply in the small intestine
- Symptoms are largely related to digestive processes and gut issues
CANDIDA OVERGROWTH
- Refers to yeast (fungal) overgrowth
- Occurs in the intestines but is also found in other parts of the body like the skin, mouth, and vaginal tract
- Symptoms include issues with digestion and also, other infections related to nails, skin, the urinary tract, mouth, and also energy, mood, and memory
Testing for Candida and SIBO
The next step would be to get the relevant tests done to figure out which one of Candida or SIBO is causing the symptoms. There are two standard tests for dysbiosis and for comprehensive functional medicine stool tests.
Dysbiosis occurs when the normal balance of fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms in the gut is disrupted. The presence of D-Arabitol, a waste product generated by Candida, in the gut can indicate IBS or IBD, as well as other gut-related symptoms associated with Candida or SIBO. These two conditions will determine whether you have Candida in your gut or SIBO.
A stool test can show if there is an overgrowth of a certain type of bacteria or yeast. This can help you figure out what is causing your symptoms. This will dictate the appropriate treatment options.
A stool that is a different color than usual may mean that you have Candida. This can be accompanied by Frothing or foaming or general looseness. It’s hard to tell if someone has Candida or SIBO just by looking at their stool because there are other infections and diseases that can cause similar symptoms.
If you have SIBO, your stool might not be a different color, but it is likely to be a different texture. This could include stool that smells bad, is floating, and might be hard to flush.
Testing for Candida Overgrowth
In addition to the above tests, you can also test for gut yeast overgrowth through regular blood tests. A complete blood count and antibodies test are also necessary for Candida. A high amount of Candida antibodies in the blood (IgG, IgA, and IgM) is probably indicative of Candida Overgrowth.
If your white blood cell count is low, it could be a sign of Candida.
Testing for SIBO Overgrowth
The breath test is important for detecting SIBO in addition to the Dysbiosis Test and Comprehensive Functional Medicine Stool Test. We spoke about how SIBO is caused by the presence of hydrogen and methane, and this test helps determine their presence.
The process is straightforward and non-invasive. A few hours after you drink a solution, your breath will be examined. The test will help to determine if the SIBO is due to high methane or high hydrogen levels. It can, however, be used in conjunction with other methods to provide a more accurate diagnosis. A breath test is not the only method that can be used to detect SIBO, but it can be used along with other methods to make the diagnosis more accurate. This test is not sufficient by itself; it must be combined with others.
In this journal, it is mentioned that Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth can be clinically diagnosed by testing small intestine fluid and culture. This test is invasive because it requires a sample of the intestine to be taken. A tube is inserted down the throat and into the small intestine.
Your healthcare practitioner will be able to advise on the tests required to diagnose small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), so this should just serve as an overview.
Treatment for Candida and SIBO
Both SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth) and Candida (a type of fungus) can cause an overgrowth of bacteria and fungi, respectively. The goal of the treatment being employed is three-pronged. The first goal is to stop the growth of harmful bacteria, and the second is to enhance the presence of good bacteria and restore the balance of microorganisms in our gastrointestinal tract. To complete the third step, you will need to seal the gut and repair it.
Treatment for Candida Overgrowth
The first thing you can do to stop the growth of candida is to cut back on refined sugars, complex carbs, and high-lactose dairy products.
To prevent Candida growth and lessen symptoms, remove alcohol and sugar from your diet and limit carbs. To prevent candida, it is necessary to avoid foods that contain yeast or sugar since these substances contribute to candida growth.
You don’t have to get rid of carbs entirely, since being on a low-carb diet for a long time can cause other health problems.
Some aspects of Candida Overgrowth can be addressed naturally. You should eat foods that help control the growth of yeast. This diet could include garlic, ginger, turmeric, olive oil, cinnamon, and apple cider vinegar, along with broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables.
You could supplement your diet with curcumin, which is found in small quantities in turmeric, or you could take it on its own. Curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties, may be helpful in treating Candida.
The text is discussing how Candida, which is a kind of fungus, can be treated by taking antifungal medication and making dietary changes. There are two main types of treatments for Candida Overgrowth: topical and oral. Topical treatments are applied directly to the affected area, while oral treatments are taken by mouth in the form of pills or tablets. For serious Candida infections that are not on the skin, doctors will need to give the patient antifungal medication through a vein.
Antifungal medicines can also be used to treat SIFO. Although they are both fungal infections, their treatment will have similarities. Specialized supplements may help improve the Candida problem by working on the intestine, by improving the gut and intestinal environment, and by boosting the effect of probiotics. The intensity of the overgrowth will determine how often these supplements need to be taken.
Lastly, Probiotics may be an important tool for dealing with Candida. Although probiotics have been studied for a long time, their importance for health is still not fully understood. They improve gut health, which might help restore the balance of yeast in the system. They also help to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria and yeast and stop them from being able to penetrate the cells in the gut or the vaginal tract. This is crucial in preventing a leaky gut.
Conclusion
It can be difficult for someone who is not a medical professional to answer the question, “Do I have SIBO or Candida?” This guide provides an overview of the questions you should ask your medical professional, signs to look out for and possible treatment options.